Hip Effusion & Fractures
Written by: Steven Chen, MD. Edited by: Jeff Greco, MD and Victor Huang, MD
Cases
Case 1: 68 yo F with history of HTN presents to the ER on a cold snowy winter night with left hip pain after a mechanical fall. Patient’s left lower extremity is slightly shortened and externally rotated, with normal distal neurovascular exam. However, X-ray of the hip appears normal.
Case 2: 6 yo M with no PMH who presents from home for refusal to bare weight on his right lower extremity. Patient is without fever or recent trauma. His right hip is slightly warm to the touch and he screams when the hip is passively flexed.
Hip Ultrasound
· In both cases above, ultrasound of the hip may be beneficial in diagnosing the disorder
· Can detect hip effusion and hematoma
· Can detect obvious or occult hip fractures that may not otherwise be picked up by plain radiographs
· Can guide hip arthrocentesis if septic joint is in the differential
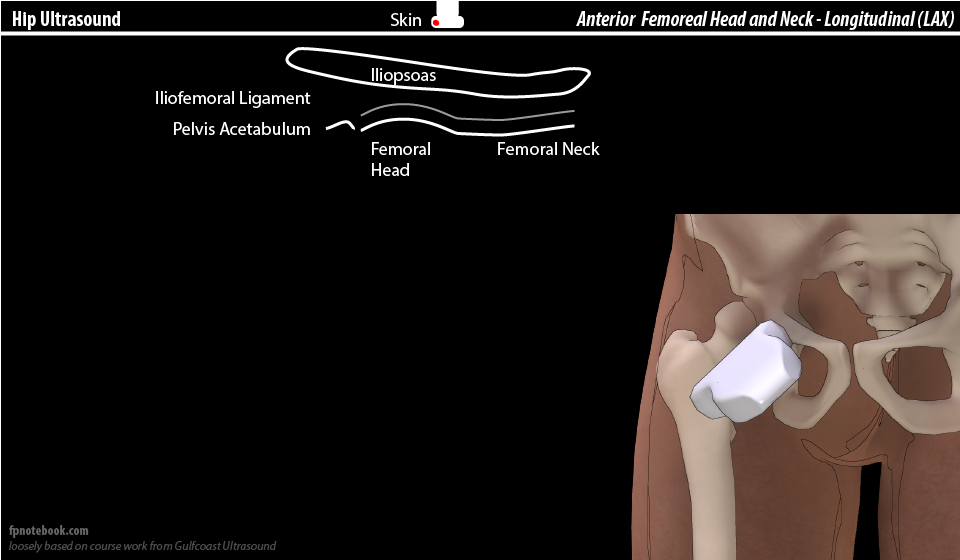
Anatomy
Technique
Use a linear transducer or a curvilinear transducer
Linear probe may be more useful in pediatric patients or those of a smaller body habitus
Curvilinear transducer may be more useful in those with a larger body habitus or anasarca
To scan the femoral head and neck: Place the probe along the axis of the femoral neck with the transducer marker pointing towards patient’s umbilicus (or acetabulum)
To scan the femoral shaft: Place the probe in a vertical axis along the shaft with probe marker pointing cephalad
A: acetabulum; FH: femoral head; I: Iliopsoas muscle; FN: femoral neck
Findings
Compare bilaterally between unaffected vs affected limb. Scan unaffected first
If fractured, will see cortical disruption on ultrasound; may present with associated hematoma/effusion
If there is an effusion, it’s usually in the joint space overlying the neck
Effusion is always abnormal in adult patient.
In pediatric it is abnormal when (depending on source):
>5-7mm
>1-2mm compared to unaffected side
In children: Normal width (mm)= 3.97 + 0.03 (height in cm)
Arthrocentesis
Sterile procedure
Same view and probe placement as the anterior approach to visualize the femoral head, neck, and the anterior synovial space
In plane approach is used as needle is inserted distally towards proximally in the same plane as the ultrasound prob
Don’t forget to use sterile ultrasound probe covers!
Summary
Ultrasound of the hip can be used to help diagnose fractures, effusions and guide your arthrocentesis to rule out septic joint.
References
· Moak JH. Hip Sonography. https://vimeo.com/46518256. Accessed Oct 30, 2020.
· Medero Colon R, Chilstrom ML. Diagnosis of an Occult Hip Fracture by Point-of-Care Ultrasound. J Emerg Med. 2015;49(6):916-919. doi:10.1016/j.jemermed.2015.06.077
· Avila J. Hip Effusion. Core Ultrasound Website. https://www.coreultrasound.com/hip-effusion/. Accessed Oct 30, 2020.
· https://ellkayblog.files.wordpress.com/2012/03/hip-anatomy.jpg. Accessed Oct 31, 2020.
· Ultrasound of the Hip and Buttocks. Ultrasoundpaedia Website. https://www.ultrasoundpaedia.com/normal-hip-groin/. Accessed Oct 30, 2020.
· Hip Ultrasound. Family Practice Notebook Website. https://fpnotebook.com/ortho/Rad/HpUltrsnd.htm. Accessed Oct 31, 2020.
· Zhe Z, Jianjin Z, Fei S, et al. Intraoperative ultrasound-guided reduction of femoral shaft fractures using intramedullary nailing: a technical note. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2019;139, 589–596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-3085-8
· Murakami AM. Ultrasound Guided Injections. Aspetar. 454-461.
· Shukla D. Intertrochanteric fracture. Youtube Website. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=moN4j7By2z4. Published Feb 8, 2017. Accessed Oct 31, 2002.
· Patel M. Femur fracture in neonate. Radiopaedia Website. https://radiopaedia.org/cases/femur-fracture-in-neonate. Accessed Oct 31, 2020.
· Tien YC, Yang CY, Chih HW. The Normal Width of Anterior Hip Synovial Recess in Children. Journal of Pediatric Orthopaedics. 2000;20(2):264-266.
· Alegria-Leal E. Ultrasound in Hip Pain and Arthrocentesis. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PPK5t8BqnVo. Published Sept 27, 2018. Accessed Oct 31, 2020.
· Hip Effusion. https://med.emory.edu/departments/emergency-medicine/sections/ultrasound/image-of-the-fortnight/soft-tissue-vascular-msk/hip_effusion.html. June 2012. Accessed Oct 31, 2020.
· Collins J, Smithuis R, Rutten M. US-guided injection of joints. Radiology Assistant Website. https://radiologyassistant.nl/musculoskeletal/ultrasound/us-guided-injection-of-joints. Published Dec 12, 2012. Accessed Oct 31, 2020.